Curious about Actual Juniper Data Center Certification (JN0-351) Exam Questions?
Here are sample Juniper Enterprise Routing and Switching, Specialist (JN0-351) Exam questions from real exam. You can get more Juniper Data Center Certification (JN0-351) Exam premium practice questions at TestInsights.
Which two mechanisms are part of building and maintaining a Layer 2 bridge table? (Choose two.)
Correct : B, C
Start a Discussions
Which two statements are correct about using firewall filters on EX Series switches? (Choose two.)
Correct : A, C
Start a Discussions
Exhibit
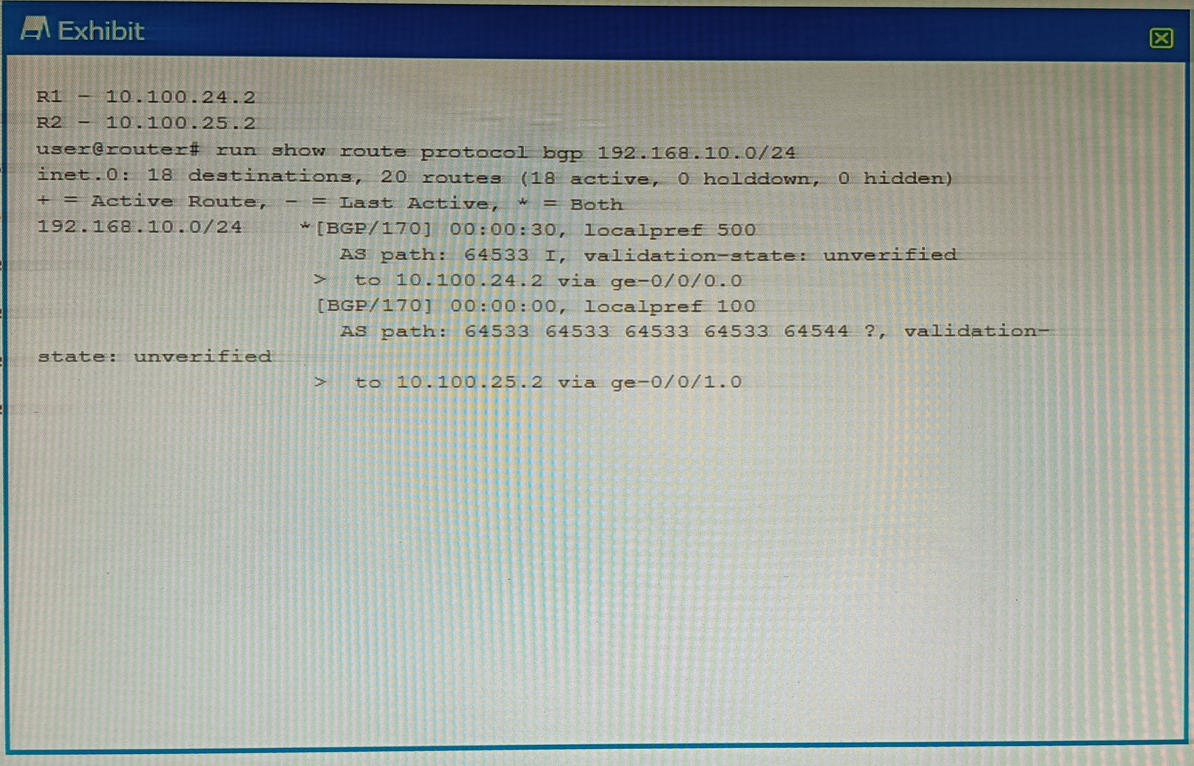
You are troubleshooting an issue where traffic to 192.168.10.0/24 is being sent to R1 instead of your desired path through R2.
Referring to the exhibit, what is the reason for the problem?
Correct : C
Start a Discussions
What are two reasons for creating multiple areas in OSPF? (Choose two.)
Correct : A, D
Option A is correct. Creating multiple areas in OSPF can help to reduce the convergence time . This is because changes in one area do not affect other areas, so fewer routers need to run the SPF algorithm in response to a change.
Option D is correct. Creating multiple areas in OSPF can help to reduce Link State Advertisement (LSA) flooding across the network. This is because LSAs are not flooded out of their area of origin.
Start a Discussions
Which two events cause a router to advertise a connected network to OSPF neighbors? (Choose two.)
Correct : A, D
Start a Discussions
Total 65 questions