Curious about Actual Juniper Cloud Certification (JN0-214) Exam Questions?
Here are sample Juniper Cloud, Associate (JN0-214) Exam questions from real exam. You can get more Juniper Cloud Certification (JN0-214) Exam premium practice questions at TestInsights.
Which two statements are correct about Network Functions Virtualization (NFV)? (Choose two.)
Correct : A, B
Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) is a framework designed to virtualize network services traditionally run on proprietary hardware. It decouples network functions from dedicated hardware appliances and implements them as software running on standard servers or virtual machines. Let's analyze each statement:
A . The NFV framework explains how VNFs fit into the whole solution.
Correct: The NFV framework provides a structured approach to deploying and managing Virtualized Network Functions (VNFs). It defines how VNFs interact with other components, such as the NFV Infrastructure (NFVI), Management and Orchestration (MANO), and the underlying hardware.
B . The NFV Infrastructure (NFVI) is a component of NFV.
Correct: The NFV Infrastructure (NFVI) is a critical part of the NFV architecture. It includes the physical and virtual resources (e.g., compute, storage, networking) that host and support VNFs. NFVI acts as the foundation for deploying and running virtualized network functions.
C . The NFV Infrastructure (NFVI) is not a component of NFV.
Incorrect: This statement contradicts the NFV architecture. NFVI is indeed a core component of NFV, providing the necessary infrastructure for VNFs.
D . The NFV framework is defined by the W3C.
Incorrect: The NFV framework is defined by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), not the W3C. ETSI's NFV Industry Specification Group (ISG) established the standards and architecture for NFV.
Why These Answers?
Framework The NFV framework provides a comprehensive view of how VNFs integrate into the overall solution, ensuring scalability and flexibility.
NFVI Role: NFVI is essential for hosting and supporting VNFs, making it a fundamental part of the NFV architecture.
JNCIA Cloud Reference:
The JNCIA-Cloud certification covers NFV as part of its cloud infrastructure curriculum. Understanding the NFV framework and its components is crucial for deploying and managing virtualized network functions in cloud environments.
For example, Juniper Contrail integrates with NFV frameworks to deploy and manage VNFs, enabling service providers to deliver network services efficiently and cost-effectively.
ETSI NFV Framework Documentation
Juniper JNCIA-Cloud Study Guide: Network Functions Virtualization
Start a Discussions
Which component of a software-defined networking (SDN) controller defines where data packets are forwarded by a network device?
Correct : D
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) separates the control plane from the data (forwarding) plane, enabling centralized control and programmability of network devices. Let's analyze each option:
A . the operational plane
Incorrect: The operational plane is not a standard term in SDN architecture. It may refer to monitoring or management tasks but does not define packet forwarding behavior.
B . the forwarding plane
Incorrect: The forwarding plane (also known as the data plane) is responsible for forwarding packets based on rules provided by the control plane. It does not define where packets are forwarded; it simply executes the instructions.
C . the management plane
Incorrect: The management plane handles device configuration, monitoring, and administrative tasks. It does not determine packet forwarding paths.
D . the control plane
Correct: The control plane is responsible for making decisions about where data packets are forwarded. In SDN, the control plane is centralized in the SDN controller, which calculates forwarding paths and communicates them to network devices via protocols like OpenFlow.
Why the Control Plane?
Centralized Decision-Making: The control plane determines the optimal paths for packet forwarding and updates the forwarding plane accordingly.
Programmability: SDN controllers allow administrators to programmatically define forwarding rules, enabling dynamic and flexible network configurations.
JNCIA Cloud Reference:
The JNCIA-Cloud certification emphasizes understanding SDN architecture and its components. The separation of the control plane and forwarding plane is a foundational concept in SDN, enabling scalable and programmable networks.
For example, Juniper Contrail serves as an SDN controller, centralizing control over network devices and enabling advanced features like network automation and segmentation.
Open Networking Foundation (ONF) SDN Architecture
Juniper JNCIA-Cloud Study Guide: Software-Defined Networking
Start a Discussions
Which cloud automation tool uses YAML playbook to install software and tools on servers?
Correct : B
Cloud automation tools streamline the deployment and management of software, tools, and infrastructure in cloud environments. Let's analyze each option:
A . Python
Incorrect: Python is a general-purpose programming language, not a cloud automation tool. While Python scripts can be used for automation, it is not specifically designed for this purpose.
B . Ansible
Correct: Ansible is a popular automation tool that uses YAML-based playbooks to define and execute tasks. It automates the installation of software, configuration management, and application deployment on servers. Ansible's simplicity and agentless architecture make it widely adopted in cloud environments.
C . Terraform
Incorrect: Terraform is an infrastructure-as-code (IaC) tool used to provision and manage cloud infrastructure (e.g., virtual machines, networks, storage). It uses HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL), not YAML, for defining configurations.
D . Heat
Incorrect: Heat is an orchestration tool in OpenStack that uses YAML templates to define and deploy cloud resources. While it supports YAML, it is specific to OpenStack and focuses on infrastructure provisioning rather than server-level software installation.
Why Ansible?
YAML Playbooks: Ansible uses YAML-based playbooks to define tasks, making it easy to read and write automation scripts.
Agentless Architecture: Ansible operates over SSH, eliminating the need for agents on target servers.
Versatility: Ansible can automate a wide range of tasks, from software installation to configuration management.
JNCIA Cloud Reference:
The JNCIA-Cloud certification covers automation tools as part of its cloud operations curriculum. Tools like Ansible are essential for automating repetitive tasks and ensuring consistency in cloud environments.
For example, Juniper Contrail integrates with Ansible to automate the deployment and configuration of network services, enabling efficient management of cloud resources.
Ansible Documentation: YAML Playbooks
Juniper JNCIA-Cloud Study Guide: Automation Tools
Start a Discussions
You just uploaded a qcow2 image of a vSRX virtual machine in OpenStack.
In this scenario, which service stores the virtual machine (VM) image?
Correct : A
OpenStack provides various services to manage cloud infrastructure resources, including virtual machine (VM) images. Let's analyze each option:
A . Glance
Correct: Glance is the OpenStack service responsible for managing and storing VM images. It provides a repository for uploading, discovering, and retrieving images in various formats, such as qcow2, raw, or ISO.
B . Ironic
Incorrect: Ironic is the OpenStack bare-metal provisioning service. It is used to manage physical servers, not VM images.
C . Neutron
Incorrect: Neutron is the OpenStack networking service that manages virtual networks, routers, and IP addresses. It does not store VM images.
D . Nova
Incorrect: Nova is the OpenStack compute service that manages the lifecycle of virtual machines. While Nova interacts with Glance to retrieve VM images for deployment, it does not store the images itself.
Why Glance?
Image Repository: Glance acts as the central repository for VM images, enabling users to upload, share, and deploy images across the OpenStack environment.
Integration with Nova: When deploying a VM, Nova retrieves the required image from Glance to create the instance.
JNCIA Cloud Reference:
The JNCIA-Cloud certification covers OpenStack services, including Glance, as part of its cloud infrastructure curriculum. Understanding Glance's role in image management is essential for deploying and managing virtual machines in OpenStack.
For example, Juniper Contrail integrates with OpenStack Glance to provide advanced networking features for VM images stored in the repository.
OpenStack Glance Documentation
Juniper JNCIA-Cloud Study Guide: OpenStack Services
Start a Discussions
Click the Exhibit button.
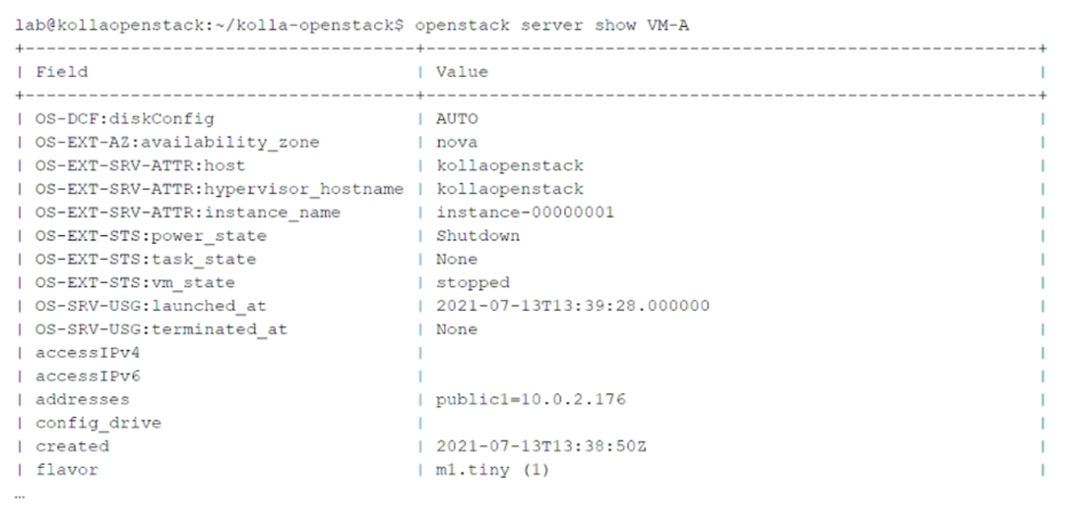
You have issued the openstack server show VM-A command and received the output shown in the exhibit.
To which virtual network is the VM-A instance attached?
Correct : B
The openstack server show command provides detailed information about a specific virtual machine (VM) instance in OpenStack. The output includes details such as the instance name, network attachments, power state, and more. Let's analyze the question and options:
Key Information from the Exhibit:
The addresses field in the output shows
public1=10.0.2.176
This indicates that the VM-A instance is attached to the virtual network named public1 , with an assigned IP address of 10.0.2.176 .
Option Analysis:
A . m1.tiny
Incorrect: m1.tiny refers to the flavor of the VM, which specifies the resource allocation (e.g., CPU, memory, disk). It is unrelated to the virtual network.
B . public1
Correct: The addresses field explicitly states that the VM-A instance is attached to the public1 virtual network.
C . Nova
Incorrect: Nova is the OpenStack compute service that manages VM instances. It is not a virtual network.
D . kollaopenstack
Incorrect: kollaopenstack appears in the output as the hostname or project name but does not represent a virtual network.
Why public1?
Network Attachment: The addresses field in the output directly identifies the virtual network (public1) to which the VM-A instance is attached.
IP Address Assignment: The IP address (10.0.2.176) confirms that the VM is connected to the public1 network.
JNCIA Cloud Reference:
The JNCIA-Cloud certification emphasizes understanding OpenStack commands and outputs, including the openstack server show command. Recognizing how virtual networks are represented in OpenStack is essential for managing VM connectivity.
For example, Juniper Contrail integrates with OpenStack Neutron to provide advanced networking features for virtual networks like public1.
OpenStack CLI Documentation: openstack server show Command
Juniper JNCIA-Cloud Study Guide: OpenStack Networking
Start a Discussions
Total 65 questions