Curious about Actual HashiCorp Security Automation (Vault-Associate) Exam Questions?
Here are sample HashiCorp Certified: Vault Associate (002) (Vault-Associate) Exam questions from real exam. You can get more HashiCorp Security Automation (Vault-Associate) Exam premium practice questions at TestInsights.
Which of the following are replication methods available in Vault Enterprise? Choose two correct answers.
Correct : C, D
The replication methods available in Vault Enterprise are performance replication and disaster recovery replication. These methods allow critical data to be replicated across clusters to support horizontally scaling and disaster recovery workloads.
Performance replication enables a primary cluster to replicate data to one or more secondary clusters, which can handle client requests and improve performance and availability. Performance replication replicates most Vault data, such as secrets, policies, auth methods, and leases, but not tokens. Performance secondaries generate their own tokens and leases, which are not replicated back to the primary. Performance replication also supports filtering, which allows selective replication of data based on namespaces or paths.
Start a Discussions
Use this screenshot to answer the question below:
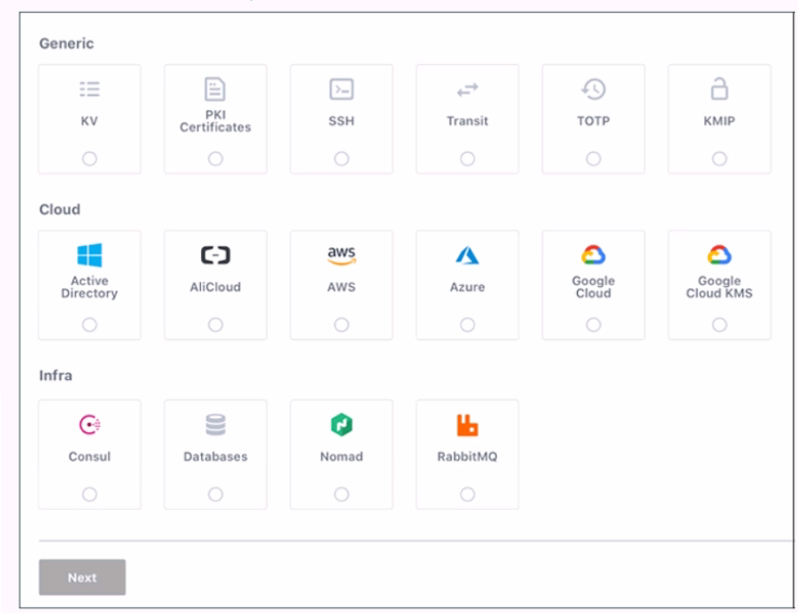
When are you shown these options in the GUI?
Correct : D
This screenshot is shown when you are enabling authentication methods in the GUI. Authentication methods are the ways users and applications authenticate with Vault. Vault supports many different authentication methods, including username and password, GitHub, and more. You can enable one or more authentication methods from the grid of options, which are divided into three categories: Generic, Cloud, and Infra. Each option has a name, a description, and a logo. You can also enable authentication methods using the Vault CLI or API.
Enabling policies, authentication engines, and secret engines are different tasks that are not related to this screenshot. Policies are rules that govern the access to Vault resources, such as secrets, authentication methods, and audit devices. Authentication engines are components of Vault that perform authentication and assign policies to authenticated entities. Secret engines are components of Vault that store, generate, or encrypt data. These tasks have different GUI pages and options than the screenshot.
[Authentication | Vault | HashiCorp Developer]
[Policies | Vault | HashiCorp Developer]
[Authentication | Vault | HashiCorp Developer]
[Secrets Engines | Vault | HashiCorp Developer]
Start a Discussions
Examine the command below. Output has been trimmed.
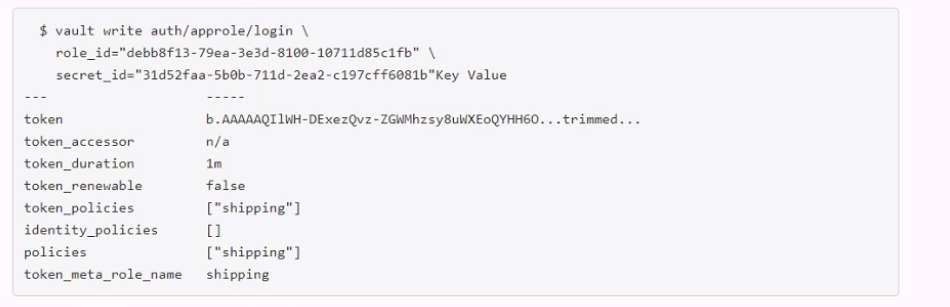
Which of the following statements describe the command and its output?
Correct : B, C
The command shown in the image is:
vault token create -policy=approle -orphan -period=60h
This command creates a new token with the following characteristics:
Start a Discussions
The key/value v2 secrets engine is enabled at secret/ See the following policy:
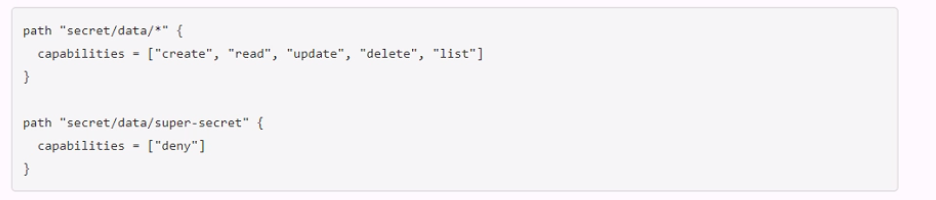
Which of the following operations are permitted by this policy? Choose two correct answers.
Correct : A, C
The policy shown in the image is:
path ''secret/data/webapp1'' { capabilities = [''create'', ''read'', ''update'', ''delete'', ''list''] }
path ''secret/data/super-secret'' { capabilities = [''deny''] }
This policy grants or denies access to the key/value v2 secrets engine mounted at secret/ according to the following rules:
Start a Discussions
Which statement describes the results of this command: $ vault secrets enable transit
Start a Discussions
Total 57 questions