Curious about Actual ARDMS Registered Diagnostic Medical Sonographer (SPI) Exam Questions?
Here are sample ARDMS Sonography Principles and Instrumentation (SPI) Exam questions from real exam. You can get more ARDMS Registered Diagnostic Medical Sonographer (SPI) Exam premium practice questions at TestInsights.
Which artifact causes a reflector to be improperly positioned on the display?
Correct : D
Acoustic Shadowing: This artifact occurs when a structure absorbs or reflects most of the ultrasound waves, causing a shadow behind the structure. It does not cause improper positioning of a reflector on the display.
Speckle: This is a form of noise in ultrasound imaging that appears as granular texture. It can affect image quality but does not lead to improper positioning of reflectors.
Enhancement: This artifact occurs when the area behind a weakly attenuating structure appears brighter. It affects the brightness of the image but does not affect the position of reflectors.
Range Ambiguity: This occurs when an echo is received after the next pulse has been sent out, causing the reflector to be placed at an incorrect depth on the display. This is because the system assumes the echo came from the most recent pulse.
'Ultrasound Physics and Instrumentation' by Frank Miele
ARDMS Sonography Principles and Instrumentation study materials
Start a Discussions
Which adjustment resulted in the change from image A to image B?
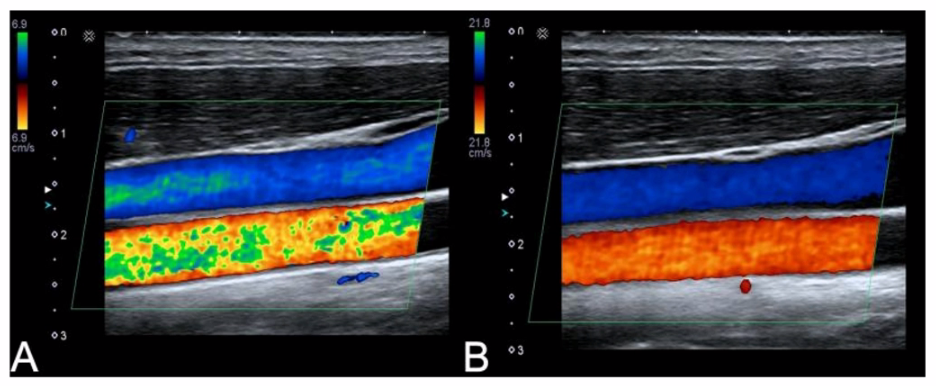
Correct : C
Increased Transmit Frequency: This would generally improve the resolution of the image but does not directly correlate to the changes seen in the provided image link.
Increased Scale: Adjusting the scale changes the velocity range displayed but does not directly affect the speckle or noise reduction.
Decreased Color Gain: Reducing the color gain can decrease the amount of color noise, making the blood flow regions more defined, which aligns with the change observed from image A to image B.
Decreased Acoustic Power: This reduces the overall intensity of the ultrasound beam, affecting penetration depth and overall brightness but is less likely to result in the specific improvements seen.
'Understanding Ultrasound Physics' by Sidney K. Edelman
ARDMS Sonography Principles and Instrumentation study materials
Start a Discussions
What are two types of cavitation in tissue?
Correct : C
Heat and Transient: Heat and transient are not classifications of cavitation.
Thermal and Mechanical: These terms refer to different bioeffects of ultrasound but are not types of cavitation.
Stable and Transient: These are the two types of cavitation observed in tissues during ultrasound. Stable cavitation involves the oscillation of gas bubbles without collapse, while transient cavitation involves the violent collapse of gas bubbles, which can generate high temperatures and shock waves.
Thermal and Stable: Thermal effects are a different concept related to tissue heating, not a type of cavitation.
'Diagnostic Ultrasound: Principles and Instruments' by Frederick W. Kremkau
ARDMS Sonography Principles and Instrumentation study materials
Start a Discussions
Which system control adjusts amplification of signals as a function of depth?
Correct : B
Time Gain Compensation (TGC), also known as Depth Gain Compensation (DGC), is used to adjust the amplification of ultrasound signals based on their depth. As ultrasound waves travel deeper into the tissue, they become weaker due to attenuation. TGC compensates for this attenuation by progressively increasing the gain for deeper echoes, ensuring that structures at different depths appear with similar brightness on the ultrasound image. This function is critical for creating a uniform image and accurately visualizing deeper anatomical structures.
American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS). Sonography Principles and Instrumentation (SPI) Examination Review Guide.
Start a Discussions
Which transducer was most likely used to create this image?
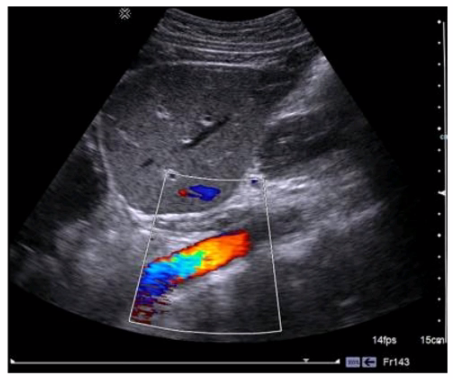
Correct : A
The image shown is typical of an abdominal ultrasound, which commonly utilizes a curvilinear transducer. Curvilinear transducers have a wider field of view at depth, making them ideal for imaging large structures within the abdomen. These transducers emit a curved beam, allowing for better penetration and a broader field of view, which is necessary for comprehensive abdominal examinations. The curvature of the image, the wide field of view, and the depth of penetration all suggest the use of a curvilinear transducer.
American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS). Sonography Principles and Instrumentation (SPI) Examination Review Guide.
Start a Discussions
Total 108 questions