Curious about Actual AICPA Business Environment and Concepts Exam Questions?
Here are sample AICPA Business Environment and Concepts (CPA-Business) Exam questions from real exam. You can get more AICPA Certified Public Accountant (CPA-Business) Exam premium practice questions at TestInsights.
Which one of the following would not be considered a carrying cost associated with inventory?
Correct : D
Choice 'd' is correct. Shipping costs (which are selling costs) would not be considered a carrying cost associated with inventory.
Choices 'a', 'b', and 'c' are incorrect. Each of the following would be considered a carrying cost associated with inventory.
A Insurance costs.
B Cost of capital invested in the inventory.
C Cost of obsolescence.
Start a Discussions
A company obtained a short-term bank loan of $500,000 at an annual interest rate of eight percent. As a condition of the loan, the company is required to maintain a compensating balance of $100,000 in its checking account. The checking account earns interest at an annual rate of three percent. Ordinarily, the company maintains a balance of $50,000 in its account for transaction purposes. What is the effective interest rate of the loan?
Correct : D
Choice 'd' is correct. 8.56%. To calculate the effective annualized percentage cost of financing:
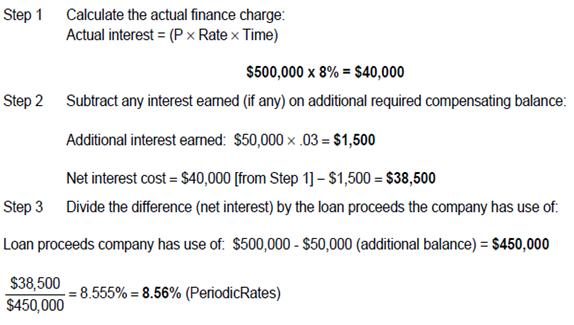
Choices 'a', 'b', and 'c' are incorrect, per the above calculation.
Start a Discussions
Which one of the following statements about trade credit is correct? Trade credit is:
Correct : C
Choice 'c' is correct. Trade credit is subject to risk of buyer default.
Choice 'a' is incorrect. Trade credit is an important source of financing for small firms.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. Trade credit is not a source of long-term financing to the seller.
Choice 'd' is incorrect. Trade credit is usually an expensive source of external financing.
Start a Discussions
CyberAge outlet, a relatively new store, is a cafe that offers customers the opportunity to browse the Internet or play computer games at their tables while they drink coffee. The customer pays a fee based on the amount of time spent signed on to the computer. The store also sells books, tee shirts, and computer accessories. CyberAge has been paying all of its bills on the last day of the payment period, thus forfeiting all supplier discounts. Shown below are data on CyberAge's two major vendors, including average monthly purchases and credit terms.
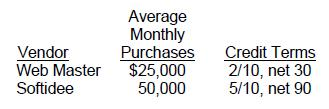
Assuming a 360-day year and that CyberAge continues paying on the last day of the credit period, the company's weighted annual interest rate for trade credit (ignoring the effects of compounding) for these two vendors is:
Correct : B
Choice 'b' is correct. 28% weighted annual interest rate.
This question pertains to a complex computation of effective rates on lost discounts for multiple terms and multiple balances. The computation of the annual percentage cost of the lost discount is equal to the effective rate of interest for the period (for example 2/10, net 30 is 2% interest charge/ 98% proceeds) times the number of times this period occurs in a year (for example 2/10, net 20 is 360 days per year divided by 20 day period during which the lost discount is used or 18 times). Extension of this logic to the referenced question involves allocating the computed annual rates to the relative balances of the outstanding payables as follows:
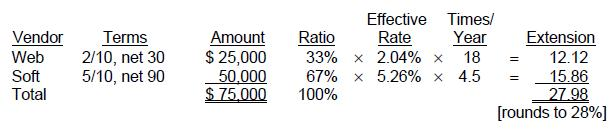
Start a Discussions
Williams, Inc. is interested in measuring its overall cost of capital and has gathered the following data. Under the terms described below, the company can sell unlimited amounts of all instruments.
* Williams can raise cash by selling $1,000, 8 percent, 20-year bonds with annual interest payments.
In selling the issue, an average premium of $30 per bond would be received, and the firm must pay floatation costs of $30 per bond. The after-tax cost of funds is estimated to be 4.8 percent.
* Williams can sell 8 percent preferred stock at par value, $105 per share. The cost of issuing and selling the preferred stock is expected to be $5 per share.
* Williams' common stock is currently selling for $100 per share. The firm expects to pay cash dividends of $7 per share next year, and the dividends are expected to remain constant. The stock will have to be underpriced by $3 per share, and floatation costs are expected to amount to $5 per share.
* Williams expects to have available $100,000 of retained earnings in the coming year; once these retained earnings are exhausted, the firm will use new common stock as the form of common stock equity financing.
* Williams' preferred capital structure is:
Long-term debt 30%
Preferred stock 20
Common stock 50
The cost of funds from retained earnings for Williams, Inc. is:
Correct : A
Choice 'a' is correct. 7.0 percent cost of funds from retained earnings.
The cost of retained earnings is equal to the rate of return required by the firm's common shareholders (or, in effect, the return 'lost' by them when the firm chooses to fund with retained earnings). While oftentimes this rate is somewhat subjective, we are given the facts to exactly answer the question in this case. The stock is currently selling for $100/share, and the dividend is given at $7/share.
$7 / $100 = 7%
Choices 'b', 'c', and 'd' are incorrect, per the above Explanation:/calculation.
Start a Discussions
Total 530 questions